继上文,我们在 TranslationServiceProvider 中已经了解几个参数设置,通过参数和自定义本地化语言数组,我们就可以直接使用【本地化】。
这样的魔力,主要还是需要归功于 Translator 类。在看这个类源代码之前,我们还是需要提前了解,在实际使用时,是如何引入本地化的。
还是上文的例子,获取模型的分页数据:
$collection = AIModel::paginate(20);
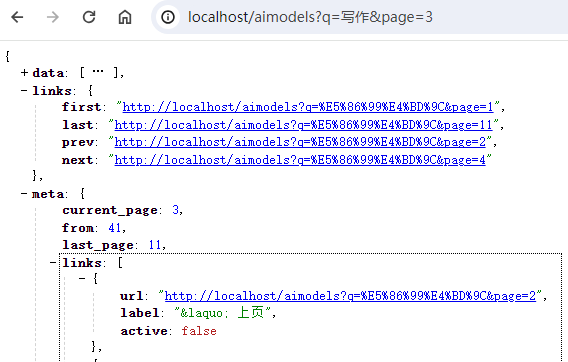
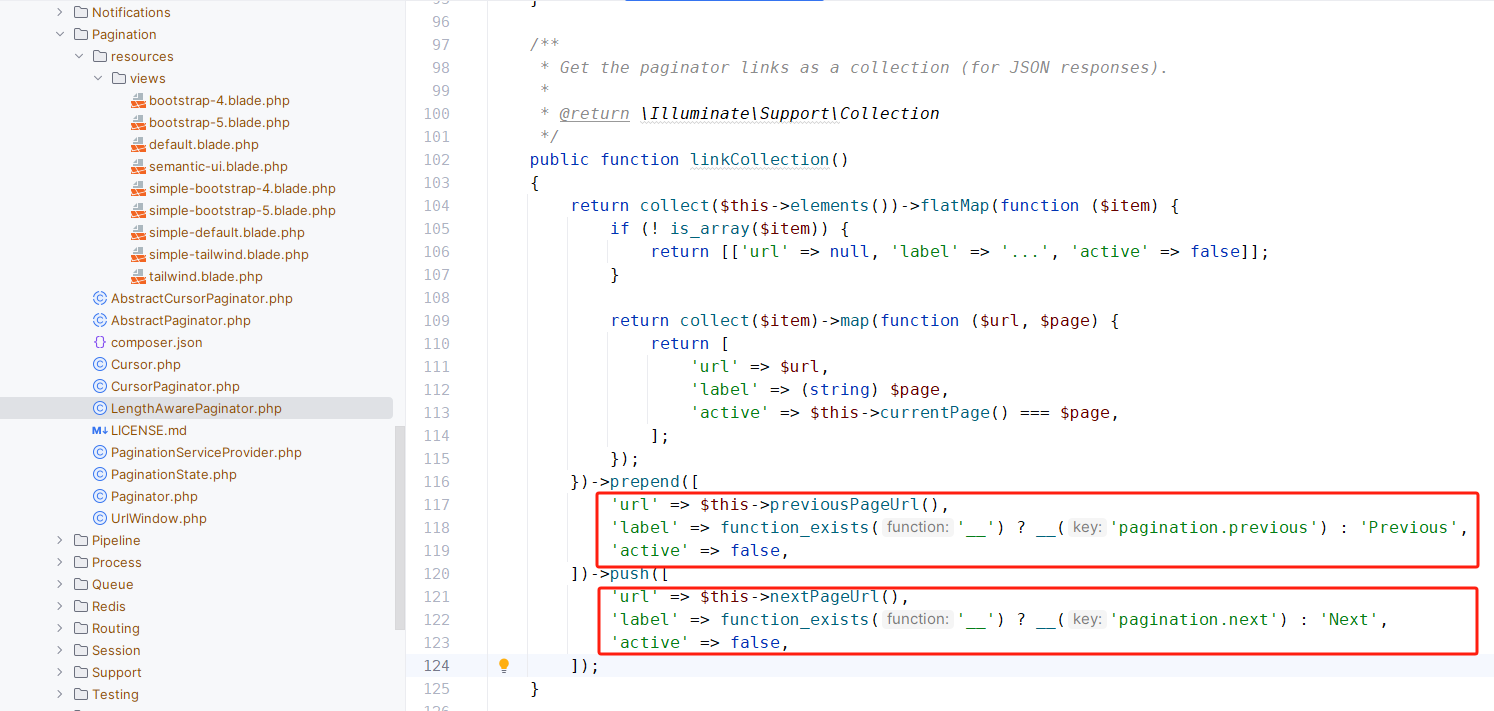
meta.links 数组里包裹着我们的分页本地化数组,具体代码可直接查看 LengthAwarePaginator,我们往下看__ 函数。
if (! function_exists('__')) {
/**
* Translate the given message.
*
* @param string|null $key
* @param array $replace
* @param string|null $locale
* @return string|array|null
*/
function __($key = null, $replace = [], $locale = null)
{
if (is_null($key)) {
return $key;
}
return trans($key, $replace, $locale);
}
}
具体看 trans 函数:
if (! function_exists('trans')) {
/**
* Translate the given message.
*
* @param string|null $key
* @param array $replace
* @param string|null $locale
* @return \Illuminate\Contracts\Translation\Translator|string|array|null
*/
function trans($key = null, $replace = [], $locale = null)
{
if (is_null($key)) {
return app('translator');
}
return app('translator')->get($key, $replace, $locale);
}
}
好了,直接看到我们的 app('translator')->get($key, $replace, $locale);,整合成一行代码就是:
__('pagination.previous')
等同于:
`app('translator')->get('pagination.previous', [], null);`
有了这条代码,我们真的就可以往下研究类 Translator 源代码了,最主要的就是其 get 函数。
/**
* Get the translation for the given key.
*
* @param string $key
* @param array $replace
* @param string|null $locale
* @param bool $fallback
* @return string|array
*/
public function get($key, array $replace = [], $locale = null, $fallback = true)
{
$locale = $locale ?: $this->locale;
// For JSON translations, there is only one file per locale, so we will simply load
// that file and then we will be ready to check the array for the key. These are
// only one level deep so we do not need to do any fancy searching through it.
$this->load('*', '*', $locale);
$line = $this->loaded['*']['*'][$locale][$key] ?? null;
// If we can't find a translation for the JSON key, we will attempt to translate it
// using the typical translation file. This way developers can always just use a
// helper such as __ instead of having to pick between trans or __ with views.
if (! isset($line)) {
[$namespace, $group, $item] = $this->parseKey($key);
// Here we will get the locale that should be used for the language line. If one
// was not passed, we will use the default locales which was given to us when
// the translator was instantiated. Then, we can load the lines and return.
$locales = $fallback ? $this->localeArray($locale) : [$locale];
foreach ($locales as $locale) {
if (! is_null($line = $this->getLine(
$namespace, $group, $locale, $item, $replace
))) {
return $line;
}
}
}
函数的第一句就是获取使用的【本地化】配置,如果函数没有传入,则以 Provider 创建时的为主:
$locale = $app->getLocale();
即,在 config/app 配置的默认中文,备选英文。
接下来就是载入本地化文件内容。
$this->load('*', '*', $locale);
等同于
public function load($locale, $group, $namespace = null)
{
if ($group === '*' && $namespace === '*') {
return $this->loadJsonPaths($locale);
}
if (is_null($namespace) || $namespace === '*') {
return $this->loadPaths($this->paths, $locale, $group);
}
return $this->loadNamespaced($locale, $group, $namespace);
}
先从 json 文件里载入我们的本地化内容,如果没有 json 文件,再从 loadNamespaced 调用。
看 return $this->loadJsonPaths($locale) 源代码,很好理解:
/**
* Load a locale from the given JSON file path.
*
* @param string $locale
* @return array
*
* @throws \RuntimeException
*/
protected function loadJsonPaths($locale)
{
return collect(array_merge($this->jsonPaths, $this->paths))
->reduce(function ($output, $path) use ($locale) {
if ($this->files->exists($full = "{$path}/{$locale}.json")) {
$decoded = json_decode($this->files->get($full), true);
if (is_null($decoded) || json_last_error() !== JSON_ERROR_NONE) {
throw new RuntimeException("Translation file [{$full}] contains an invalid JSON structure.");
}
$output = array_merge($output, $decoded);
}
return $output;
}, []);
}
推荐,这个作为我们自己写代码时,可以直接引用,把 json 文件内容转为数组格式。代码通俗易懂。
由于,我们直接使用 pagination.php 数组代码形式,我们继续看源代码:
/**
* Load a locale from a given path.
*
* @param array $paths
* @param string $locale
* @param string $group
* @return array
*/
protected function loadPaths(array $paths, $locale, $group)
{
return collect($paths)
->reduce(function ($output, $path) use ($locale, $group) {
if ($this->files->exists($full = "{$path}/{$locale}/{$group}.php")) {
$output = array_replace_recursive($output, $this->files->getRequire($full));
}
return $output;
}, []);
}
这个和 json 文件的形式有的一拼,就是把 php 文件的数组读取出来就是。
到此,我们知道了如何读取本地化数组内容了,剩下的无非就是数组合并,看看默认 vendor 的初始代码中是否有默认值。
最后,就是备选翻译的使用,如果本地化翻译不存在时,就需要调用备选方案,道理还是一样的,代码再走一遍。
$line = $this->loaded['*']['*'][$locale][$key] ?? null;
// If we can't find a translation for the JSON key, we will attempt to translate it
// using the typical translation file. This way developers can always just use a
// helper such as __ instead of having to pick between trans or __ with views.
if (! isset($line)) {
[$namespace, $group, $item] = $this->parseKey($key);
// Here we will get the locale that should be used for the language line. If one
// was not passed, we will use the default locales which was given to us when
// the translator was instantiated. Then, we can load the lines and return.
$locales = $fallback ? $this->localeArray($locale) : [$locale];
foreach ($locales as $locale) {
if (! is_null($line = $this->getLine(
$namespace, $group, $locale, $item, $replace
))) {
return $line;
}
}
}
这里就不在赘述了,相信你也能看得懂。
Translation 组件源代码的解读基本就这样了,总结一下:
- 在
config/app配置中设置需要的本地化语言和备选语言; - 在
lang目录中写好对应的翻译内容,可以是json和php数组格式; - 在需要的地方使用辅助函数调用:
__和trans,或者还有其他方式。
如果觉得文章内容对您有用 打赏
